【2025】Estimating urban building height based on smartphone GNSS LOS/NLOS signal classification.
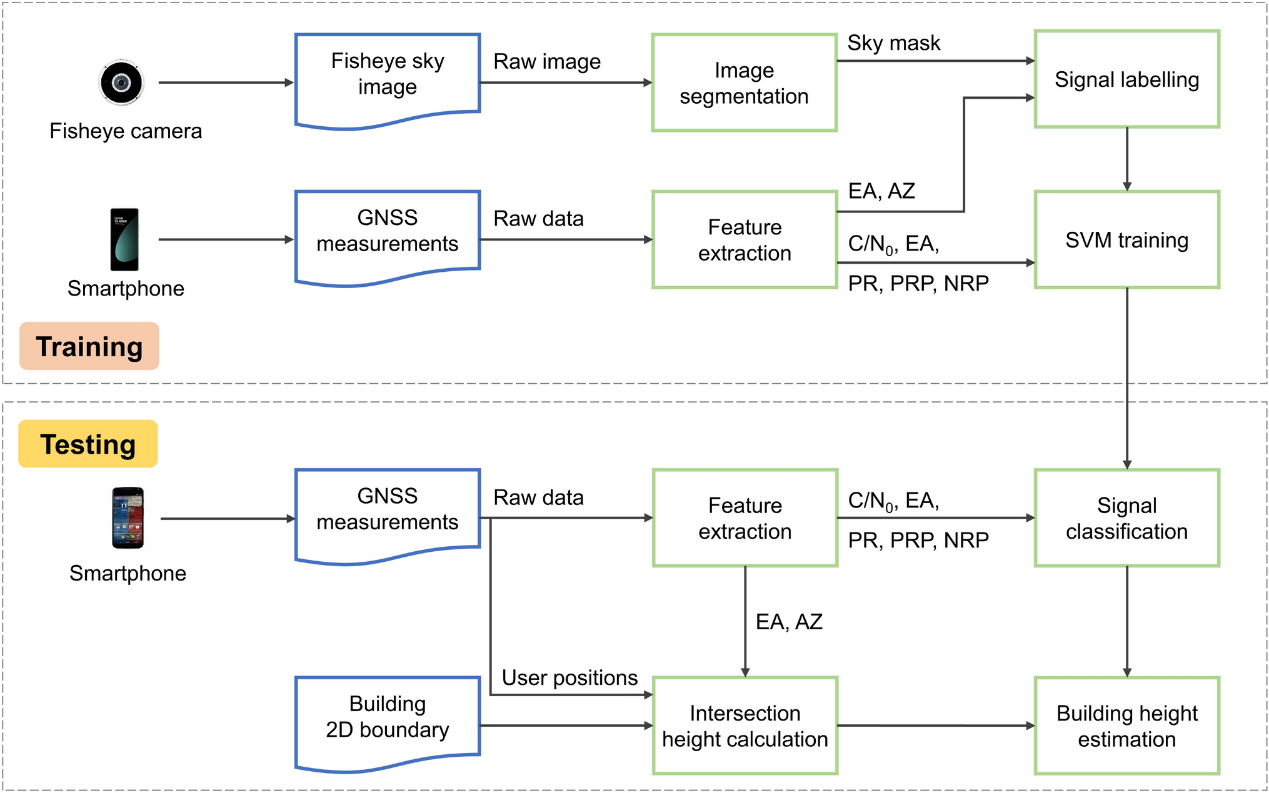
3D building maps have been urgently demanded in numerous applications such as urban planning and disaster monitoring. Conventional LiDAR and visual-based 3D building mapping techniques face challenges like high financial cost and human resource consumption for large-scale 3D map construction and update. Recently, global navigation satellite system (GNSS)-based urban mapping has received much attention, owing to the inherent advantages like wide coverage area, high update efficiency, and low cost. However, most of the existing GNSS mapping approaches merely exploit the single feature of signal power, and cannot provide satisfactory mapping accuracy. In this article, an urban building height estimation method based on smartphone GNSS data is developed, resorting to the machine learning-based GNSS line-of-sight (LOS)/non-line-of-sight (NLOS) classifier. The supervised support vector machine (SVM) uses multiple GNSS signal features extracted from raw data to achieve the LOS/NLOS signal classification. The building height, around which the signal LOS/NLOS condition changes drastically, is estimated by applying a logistic function fitting to the signal LOS probability along the altitude direction. The critical building height estimations in conjunction with a priori database of the 2D building boundaries produce the 3D building map. Experimental campaigns under four different building scenarios are performed to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. Experimental results reveal that the proposed smartphone GNSS LOS/NLOS classification-based approach yields an absolute building height estimation error lower than 2.3 m, as against 21.5 m provided by the existing GNSS building mapping algorithm.
引用格式如下:
 时间:2025-06-01
时间:2025-06-01 浏览:10
浏览:10