【2025】Integer ambiguity validation through machine learning for precise point positioning.
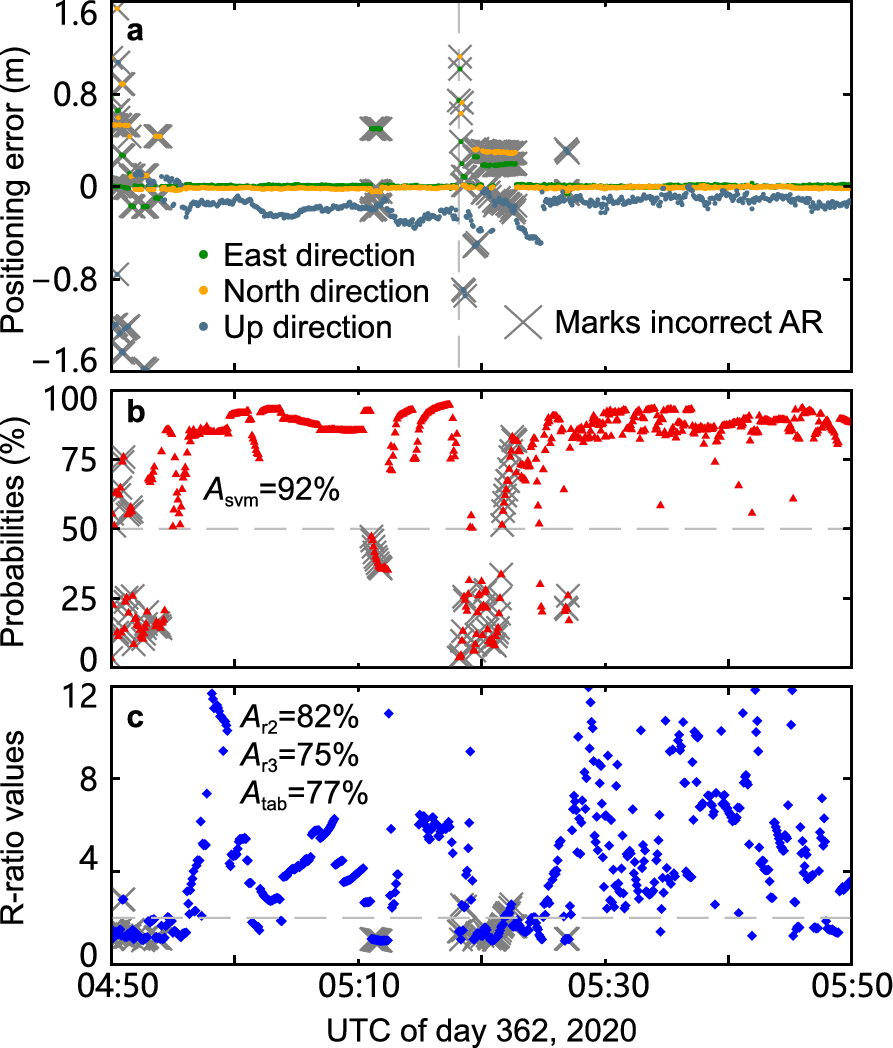
The discrimination test of ambiguity resolution, also known as ambiguity validation, is a vital procedure to quantify the reliability of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) ambiguity-fixed solutions. Several well-known tests, including the R-ratio, W-ratio, and Ambiguity Dilution of Precision, usually employ empirical thresholds for the discrimination of integer candidates. We aim at improving the reliability of ambiguity validation by integrating these tests using a machine learning model called the Support Vector Model (SVM). The dataset used consists of simulated real-time Precise Point Positioning Ambiguity Resolution (PPP-AR) solutions in 1-day batch. Specifically, the training dataset is derived using the observations from days 1–31 of year 2023, while the testing dataset is generated using the observations from days 153–159 of years 2022 and 2024. The results reveal that the SVM validates PPP-AR at a success rate of 83% for the independent testing dataset. At the same time, the mean error of the convergence time predicted by the SVM is about 1.0 min, whereas that by the R-ratio test up to 5.0 min. A vehicle-borne experiment conducted on day 362 of year 2020 further demonstrates the improvement of this method in a kinematic scenario, with a success rate of 92% compared to 82% with the conventional R-ratio test.
引用格式如下:
 时间:2025-06-01
时间:2025-06-01 浏览:9
浏览:9