Wuhan combination center
1. Background
The Wuhan Combination Center (WCC) was formally approved by the IGS Governing Board (GB) in 2024. It aims at providing combined high-precision and highly-reliable multi-GNSS satellite products. The priorities of the WCC include: (1) The WCC serves as a backup combination institution; (2) The WCC incorporates the MGEX or demonstration products into the combination; (3) The WCC combined products contain all-frequency code/phase biases to avoid day-boundary discontinuity.
The tasks of the WCC are:
(1) The WCC will focus on combining orbit, clock, and code/phase bias products, covering ultra-rapid, rapid, and final product lines;
(2) Combined products for GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo will be released initially and BDS/QZSS will be introduced later;
(3) PPP-AR validation will be carried out to monitor the quality and reliability of combined products. The WCC will enhance the consistency, interoperability, and reliability of AC-specific GNSS products, addressing the challenges in areas such as time and frequency transfer, geodesy, and satellite positioning.
2. Content
(1) work orientation
Wuhan Combination Center (WCC) is one of the two major satellite product combination centers in the world, together with JPL, and is mainly responsible for satellite product combination, testing and publicity, including:
Product combination of orbits, clock, bias etc;
Product combination covering ultra-rapid, rapid and final products;
Product combination covering OPS and MGEX products;
Product quality validation and PPP/PPP-AR test for the combined products;
Responsible for the promotion of combined products.
However, different from IGS Analysis Center Coordinator, WCC aims at innovation and practice, and will absorb more types of products, develop more performance, and find more possibilities in satellite product development. Compared with ACC, there are mainly the following differences in the work content:
The combination will include more potential AC products;
Pioneering multi-GNSS product combination;
Adding MGEX products to the daily combination;
bias combination with the final combined product supporting user PPP-AR;
The combined products will be aligned to eliminate day boundary discontinuities.
WCC will strive to do better than ACC in precision satellite product synthesis, and conduct more in-depth exploration and research around the BDS satellite, phase bias products, and day-boundary discontinuities.
(2) Summary of results
Address:https://igs.org/wg/wcc
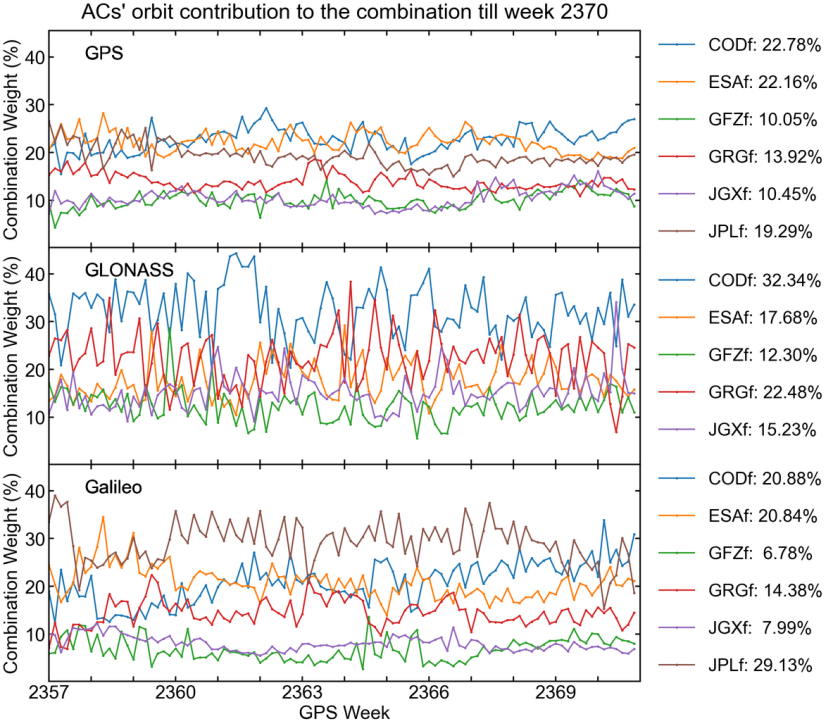
Orbit combination weight
The orbit combination employs an ACs-wise weighting method in which the weight assigned to a specific product depends on its consistency in relation to the combined orbit.
ACs’ transformation parameters
The differences in satellite orbits, relative to the combined orbit coordinate frame for each AC, are expressed in terms of seven parameters.

The weekly orbit RMSE
The orbit RMSE refers to the daily RMSE of orbit for each AC with respect to the combined orbit, which reflects the precision of orbit combination and the consistency between individual ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products and a slash inside means an outlier excluded from the combination. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC orbit for this week.

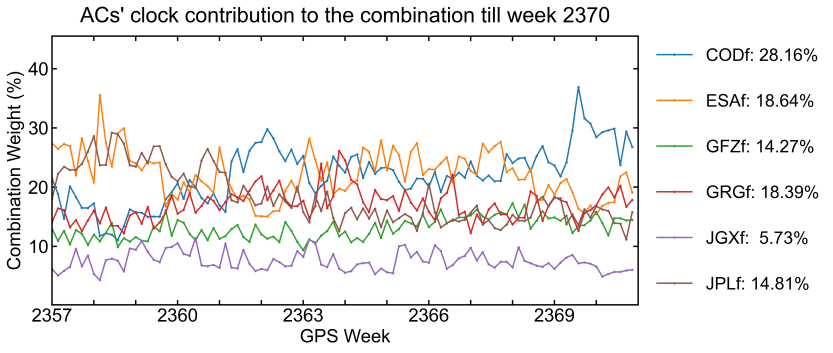
Clock/bias combination weight
The clock combination employs an iterative weighting method in which the weight assigned to a specific product depends on its residuals in relation to the combined clock.
The weekly clock/bias RMSE
The clock/bias RMSE refers to the daily RMSE of clock/bias for each AC with respect to the combined integer clock, which reflects the precision of clock and bias combination and the consistency between individual ACs. Each grid represents a satellite on a particular day. Blank grids mean unavailable products and a slash inside means an outlier excluded from the combination. The line chart below shows the satellite clock outlier rate per day for each AC, with gray block indicating that relevant satellite clocks do not participate in the comparison. The statistics at the bottom indicate the overall RMSE of AC clock/bias for this week.

The clock/bias Allan Deviation
Modified Allan Deviation (MDEV) is used to characterize the frequency stability and noise properties of the clock. Different curves represent products from different analysis centers. Comprehensive products are indicated in bold red, respectively, the smaller the MDEV, the better the stability of the clock products.

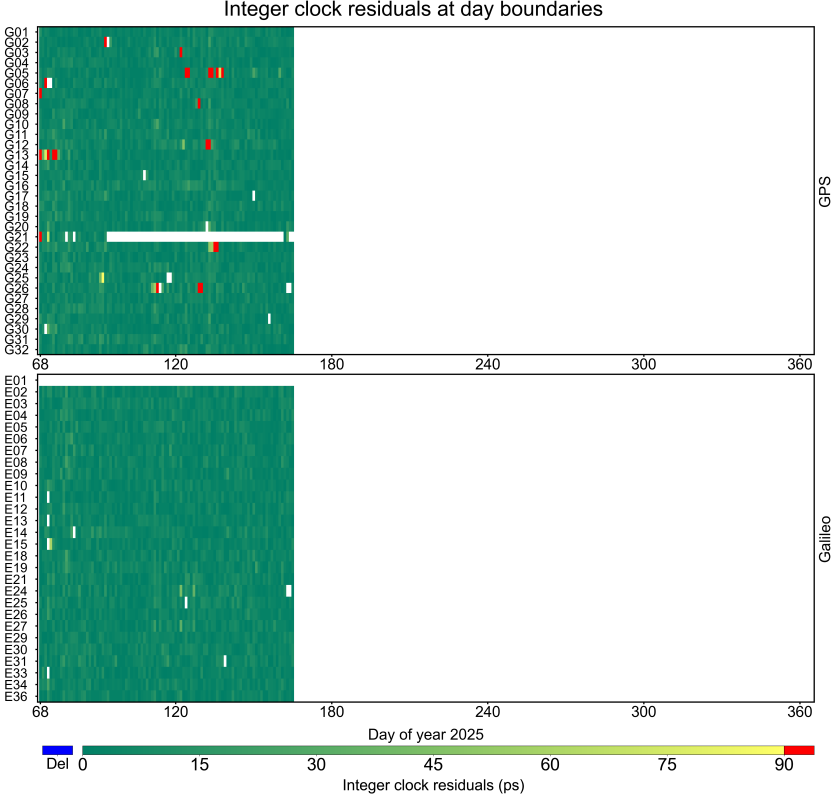
Day boundary discontinuity
Day boundary discontinuity refers to the difference between the clock at 24:00:00 and its counterpart the next day at 00:00:00. The image shows the cumulative day boundary discontinuity of the WCC products to date to reflect the overall continuity of the WCC.
PPP-AR validation
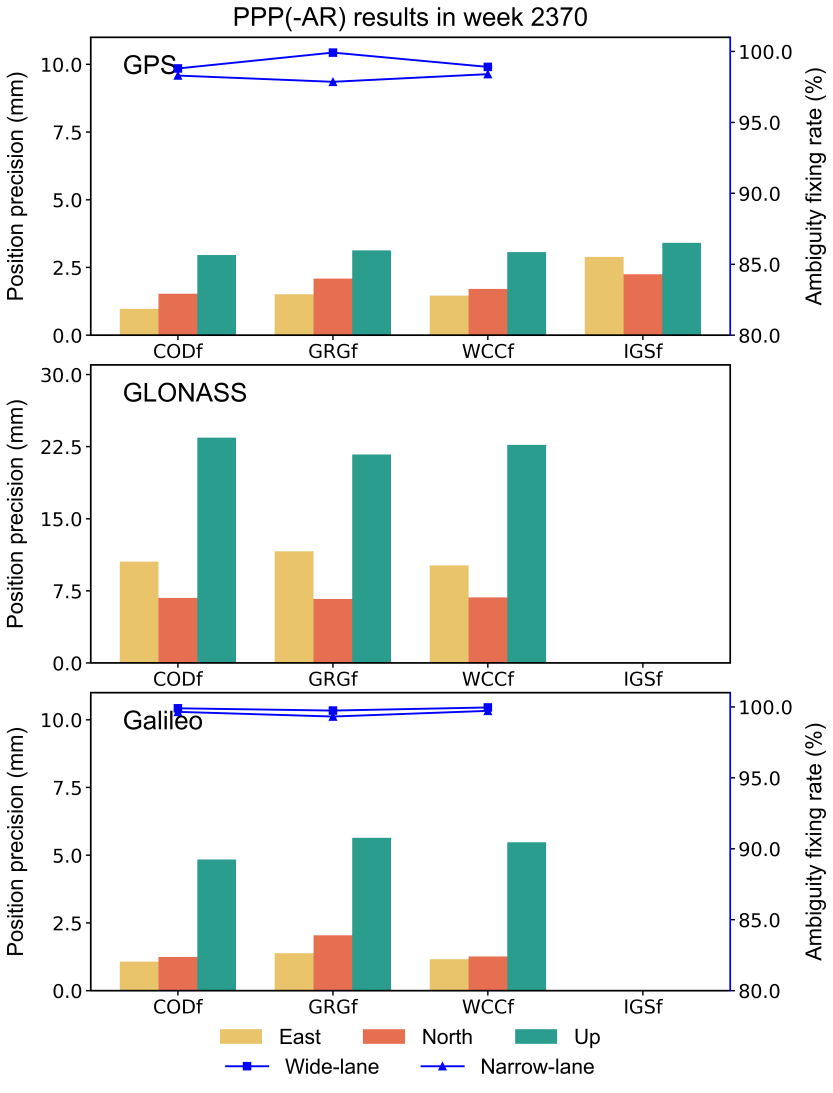
The GPS/Galileo data with a sampling interval of 300 s from 10 globally distributed stations are processed for PPP-AR in a static mode with the PRIDE PPP-AR software. The fixing rate and position precision of each single constellation solution are presented in the figure below. IGS daily SINEX products are used as reference solution. “WCC” stands for the combined products.
(3) Products download address
ftps://bdspride.com
简易脚本:curl --ftp-ssl -k -O ftps://bdspride.com/wcc/${week}/${filename}
week和filename分别代表GPS周和文件名。
如week=2369,filename=WCC0OPSFIN_20251590000_01D_01D_OSB.BIA.gz
(4) WCC members
The following table lists those who support the PPP-AR Working Group program and are willing to contribute products and/or expertise. This list may grow as more people become aware of the Working Group.

3. Reference
[1] Chen G, Guo J, Geng T, et al. Multi-GNSS orbit combination at Wuhan University: strategy and preliminary products[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2023, 97(5): 41.
[2] Geng J, Yan Z, Wen Q, et al. Integrated satellite clock and code/phase bias combination in the third IGS reprocessing campaign[J]. GPS solutions, 2024, 28(3): 150.
 时间:2025-07-10
时间:2025-07-10 浏览:9
浏览:9